mathdial
🧮 MathDial: A Dialogue Tutoring Dataset with Rich Pedagogical Properties Grounded in Math Reasoning Problems
🧮 MathDial is grounded in math word problems as well as student confusions which provide a challenging testbed for creating faithful and equitable dialogue tutoring models able to reason over complex information. Current models achieve high accuracy in solving such problems but they fail in the task of teaching.
Description
While automatic dialogue tutors hold great potential in making education personalized and more accessible, research on such systems has been hampered by a lack of sufficiently large and high-quality datasets. Collecting such datasets remains challenging, as recording tutoring sessions raises privacy concerns and crowdsourcing leads to insufficient data quality. To address this, we propose a framework to generate such dialogues by pairing human teachers with a Large Language Model (LLM) prompted to represent common student errors. We describe how we use this framework to collect 🧮 MathDial, a dataset of 3k one-to-one teacher-student tutoring dialogues grounded in multi-step math reasoning problems. While models like GPT-3 are good problem solvers, they fail at tutoring because they generate factually incorrect feedback or are prone to revealing solutions to students too early. To overcome this, we let teachers provide learning opportunities to students by guiding them using various scaffolding questions according to a taxonomy of teacher moves. We demonstrate 🧮 MathDial and its extensive annotations can be used to finetune models to be more effective tutors (and not just solvers). We confirm this by automatic and human evaluation, notably in an interactive setting that measures the trade-off between student solving success and telling solutions. The dataset is released publicly.
Dataset
The dataset is available in the data folder. It contains all 2861 conversations.
The dataset is split into train and test - see data/train.csv and data/test.csv (for csv format).
For jsonl format, see data/train.jsonl and data/test.jsonl. To see a small sample of the dataset, look at data/example.jsonl
Please note that each row in the file consists of full conversations between a teacher and a student delimited with special |EOM| notation.
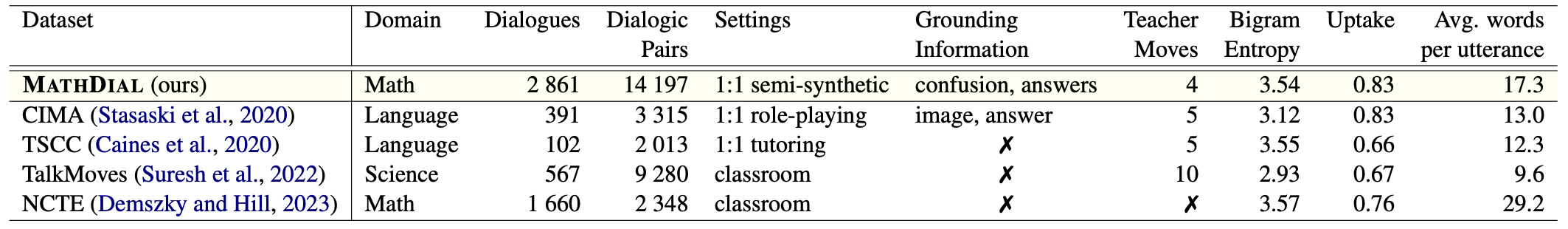
Data Structure
qid- unique identifier of the problemscenario- order of the problem in the data collection, out of the 5 scenarios in a sessionquestion- math problem textground_truth- correct answer to the problemstudent_incorrect_solution- student incorrect solution to the problem caused by some confusionstudent_profile- student profile based on general math problem solving student misconceptionsteacher_described_confusion- teacher annotated student confusion in free textself-correctness- teacher annotated whether student solved the problem correctly by the end of the conversation- options:
Yes,Yes, but I had to reveal the answer,No
- options:
self-typical-confusion- teacher annotated whether student exhibited a typical 7th grade confusion, Likert scale 1 (unlikely) to 5 (very likely)self-typical-interactions- teacher annotated whether student exhibited typical 7th grade interactions, Likert scale 1 (unlikely) to 5 (very likely)conversation- conversation in a string format with|EOM|delimiter between Teacher and Student personasPersona: (dialog_act) texte.g.Teacher: (focus) What is the difference?|EOM|Student: I mean ...|EOM|Teacher:
HuggingFace Loader
Setup your environment
pip install -r requirements.txt
echo "For implementing teacher and student models, access to OpenAI API is needed."
export OPENAI_API_KEY="<your-openai-api-key>"
Teacher model - Generate next tutor response
python interactivetutoring/gpt_baseline.py --input_file "<dataset-path>" --model_name "<name-of-your-model>" --max_utterances "<stopping-point>" --export_file "<export-file-with-conversations>"
Example using ChatGPT3.5 as a teacher model on a small data sample:
python interactivetutoring/gpt_baseline.py --input_file "data/example.jsonl" --model_name "chatgpt_baseline" --max_utterances 5 --export_file "output/chatgpt_baseline.jsonl"
Please see interactivetutoring/teachers.py how to add your own teacher model.
Evaluate your teacher model using simulated student
python interactivetutoring/evaluate.py --input_file "<path-to-file-with-generations>" --model_name "<model-name>"
Example using dummy data:
python interactivetutoring/evaluate.py --input_file "output/example_model_output.jsonl" --model_name "chatgpt_baseline"
Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT)
To train the model using SFT, navigate to the SFT_Finetuning folder and run the script. Or run the following command:
cd SFT_Finetuning
python SFT_Finetuning.py
This will fine-tune the Qwen/Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct model on the MathDial dataset. The model is available at Huggingface eth-nlped/MathDial-SFT-Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct.
Citation
Please cite the following:
Jakub Macina, Nico Daheim, Sankalan Chowdhury, Tanmay Sinha, Manu Kapur, Iryna Gurevych, and Mrinmaya Sachan. 2023. MathDial: A Dialogue Tutoring Dataset with Rich Pedagogical Properties Grounded in Math Reasoning Problems. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2023, pages 5602–5621, Singapore. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Example

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
